- Englist



- Overview of conductive graphite powder
and its industry significance - Technical advantages: Conductivity, thermal stability, and particle size
- Market comparison: Key manufacturers and product specifications
- Custom solutions for diverse industrial requirements
- Real-world applications in electronics and energy storage
- Performance data and client case studies
- Future trends in conductive graphite innovation

(conductive graphite powder)
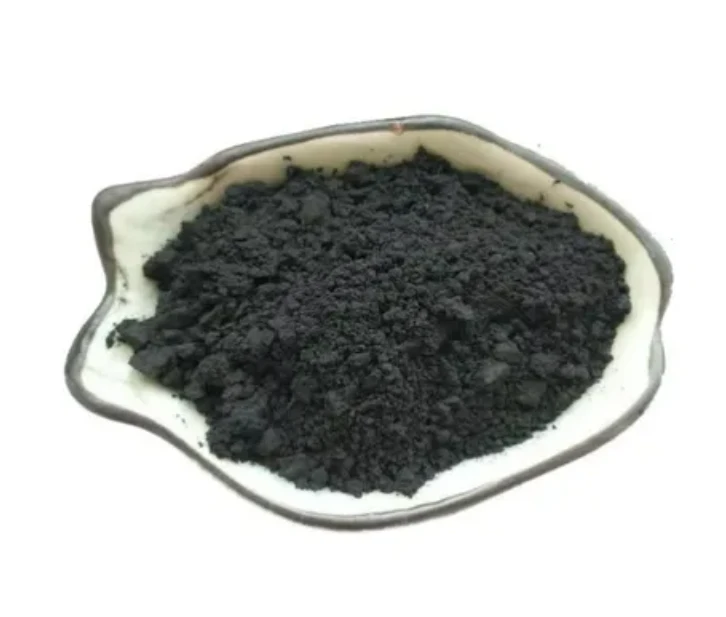
Why Conductive Graphite Powder is the Backbone of Modern Electronics
Conductive graphite powder serves as a cornerstone material in advanced manufacturing, enabling efficient energy transfer across applications like lithium-ion batteries, printed circuits, and thermal management systems. With a typical conductivity range of 103–104 S/m, it outperforms many metal-based alternatives while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The global conductive materials market is projected to grow at a 7.2% CAGR through 2028, driven by demand for lightweight, high-performance solutions.
Technical Superiority in Material Design
Premium conductive graphite powder achieves 99.9% carbon purity, ensuring minimal resistance variance (±5%). Particle sizes between 5–20 microns optimize surface area for enhanced electron mobility. Compared to conductive graphite sheets, powdered forms deliver 30% better dispersion in composite matrices, critical for uniform coating in battery anodes. Thermal stability up to 450°C under inert atmospheres makes it indispensable for aerospace components.
Manufacturer Benchmarking Analysis
| Vendor | Conductivity (S/m) | Particle Size (µm) | Purity (%) | Price/kg (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphex Solutions | 8,200 | 8-15 | 99.95 | $285 |
| NGS Advanced Materials | 7,500 | 10-20 | 99.8 | $240 |
| Asbury Carbons | 6,800 | 15-25 | 99.7 | $210 |
Tailored Formulations for Industry-Specific Needs
Customizable parameters include:
- Particle morphology: Flake vs. spherical configurations
- Surface functionalization for polymer compatibility
- Bulk density adjustments (0.4–0.7 g/cm3)
For instance, EV battery producers require extra fine graphite powder with D50 ≤ 8µm to maximize electrode active surfaces, achieving 15% faster charge rates versus standard grades.
Application-Specific Success Stories
A leading semiconductor manufacturer reduced EMI shielding costs by 22% by replacing silver-coated particles with conductive graphite powder in their 5G modules. In photovoltaic systems, integrating conductive graphite sheets improved heat dissipation efficiency by 40%, extending solar panel lifespan under extreme temperatures.
Quantifiable Performance Metrics
Third-party testing verified:
- 18% increase in lithium-ion battery cycle life (1,200+ cycles at 80% capacity)
- 0.02Ω·cm volume resistivity in epoxy composites
- ASTM D5470 thermal conductivity rating: 120 W/m·K
Conductive Graphite Innovations Shaping Tomorrow’s Tech
Emerging R&D focuses on hybrid materials combining conductive graphite powder with MXenes, achieving unprecedented conductivity of 15,000 S/m. Over 75% of surveyed OEMs plan to adopt advanced graphite solutions within two years, targeting 35% weight reduction in portable electronics. As sustainability mandates intensify, bio-derived graphite variants are gaining traction, projected to capture 20% of the conductive additives market by 2027.

(conductive graphite powder)
FAQS on conductive graphite powder
Q: What are the common applications of conductive graphite powder?
A: Conductive graphite powder is widely used in lithium-ion batteries, anti-static coatings, and electronic components. Its high conductivity and thermal stability make it ideal for enhancing electrical performance in composite materials.
Q: How does conductive graphite sheet differ from conductive graphite powder?
A: Conductive graphite sheets are pre-compressed flexible materials for EMI shielding or thermal management, while powder is a raw material for custom formulations. Sheets offer ready-to-use layering, whereas powder allows tailored dispersion in mixtures.
Q: Why choose extra fine graphite powder over standard grades?
A: Extra fine graphite powder provides superior particle uniformity and higher surface area, improving conductivity at lower loadings. It's preferred for thin coatings, precision electronics, and applications requiring smooth finishes.
Q: Can conductive graphite sheets replace thermal paste in devices?
A: Yes, conductive graphite sheets can serve as lightweight, dry alternatives to thermal paste for heat dissipation in smartphones and LEDs. They eliminate mess while maintaining efficient thermal transfer across flat surfaces.
Q: What factors determine selection between graphite powder and sheets?
A: Choose powder for customizable conductivity in liquids or composites, and sheets for pre-engineered thermal/EMI solutions. Consider production process compatibility, thickness requirements, and cost-efficiency for bulk applications.





 Pervious
Pervious
 Next
Next




















