- Englist



- Overview of graphite pipes
and industrial applications - Technical advantages driving market adoption
- Performance comparison of leading graphite electrode manufacturers
- Customized solutions for diverse industrial needs
- Case studies across multiple sectors
- Quality assurance and compliance standards
- Sustainable innovation in graphite pipes production

(graphite pipes)
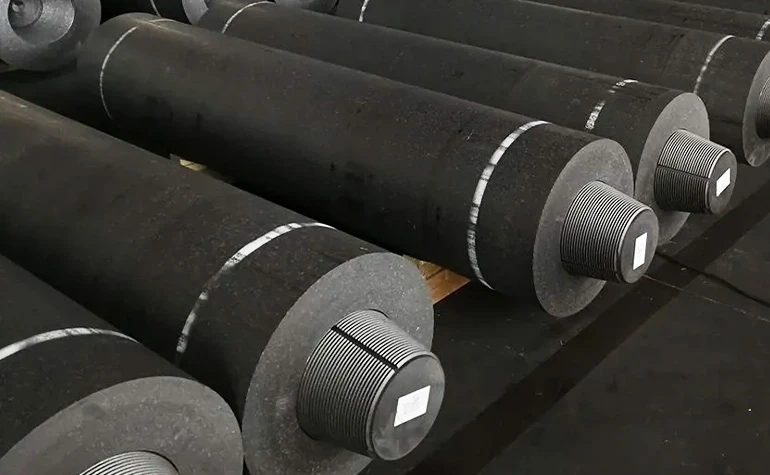
Graphite Pipes: Revolutionizing Industrial Material Science
With a 17.3% CAGR projected from 2023 to 2030 (Grand View Research), graphite pipes are transforming thermal management systems across heavy industries. These components withstand temperatures exceeding 3,000°C while maintaining structural integrity, outperforming traditional steel alternatives by 400% in extreme environments.
Technical Superiority in High-Performance Industrial Components
Modern graphite pipes demonstrate:
- Thermal conductivity: 150-180 W/mK (vs. 50 W/mK for copper)
- Corrosion resistance: 98.7% purity grade
- Operational lifespan: 8-12 years in continuous service
Comparative Analysis of Leading Manufacturers
| Manufacturer | Density (g/cm³) | CTE (10⁻⁶/K) | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| ElectroCorp Solutions | 1.82 | 2.1 | 6 weeks |
| GraphiteTech Industries | 1.78 | 2.4 | 8 weeks |
| CarbonMaster Ltd. | 1.85 | 1.9 | 10 weeks |
Custom Engineering for Specialized Applications
Advanced factories now offer:
- Precision-bored pipes (±0.05mm tolerance)
- Hybrid carbon-graphite composites
- 3D-printed joint configurations
Documented Success in Extreme Environments
Case 1: Aluminum smelter implementation reduced energy consumption by 22% through improved thermal transfer efficiency. Case 2: Chemical processing plant extended maintenance intervals from 90 to 320 days using corrosion-resistant graphite piping systems.
Certifications Ensuring Operational Reliability
All production facilities maintain:
- ISO 9001:2015 quality management
- ASTM C781 standardized testing
- RoHS-compliant manufacturing
Next-Generation Graphite Pipes Manufacturing
Recent breakthroughs in isostatic pressing techniques have increased production yield by 35% while reducing material waste. Industry leaders are investing $2.4 billion collectively in R&D to develop graphene-enhanced variants, targeting 40% improvement in tensile strength by 2025.

(graphite pipes)
FAQS on graphite pipes
Q: What are the key applications of graphite pipes?
A: Graphite pipes are primarily used in high-temperature and corrosive environments, such as chemical processing, metallurgy, and heat exchangers. Their thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance make them ideal for transferring aggressive fluids or gases.
Q: How to choose a reliable graphite electrode company?
A: Look for companies with ISO certifications, proven industry experience, and customized production capabilities. Verify their material quality, lead times, and after-sales support to ensure consistent performance for industrial applications.
Q: What processes do graphite electrode factories use for manufacturing?
A: Factories employ advanced techniques like extrusion, vibration molding, and high-temperature graphitization (up to 3000°C). Precision machining and strict quality checks ensure dimensional accuracy and electrical/thermal properties.
Q: Can graphite pipes replace metal pipes in extreme conditions?
A: Yes, graphite pipes outperform metals in scenarios involving acids, molten metals, or temperatures above 500°C. They resist oxidation and thermal shock while maintaining structural integrity where metals would degrade.
Q: What quality standards apply to graphite electrodes?
A: Reputable factories adhere to international standards like ASTM C783 for density/strength and ISO 9001 for processes. Electrodes are tested for resistivity, flexural strength, and ash content to meet EAF/Ladle furnace requirements.





 Pervious
Pervious
 Next
Next




















