- Englist



- Understanding the Core Properties of Flexible Graphite Sheets
- Technical Advantages Over Traditional Thermal Materials
- Market Analysis: Leading Manufacturers Compared
- Tailored Solutions for Industry-Specific Needs
- Performance Metrics: Data-Driven Insights
- Real-World Applications Across Key Sectors
- Future Trends in Flexible Graphite Sheet Technology

(flexible graphite sheet)
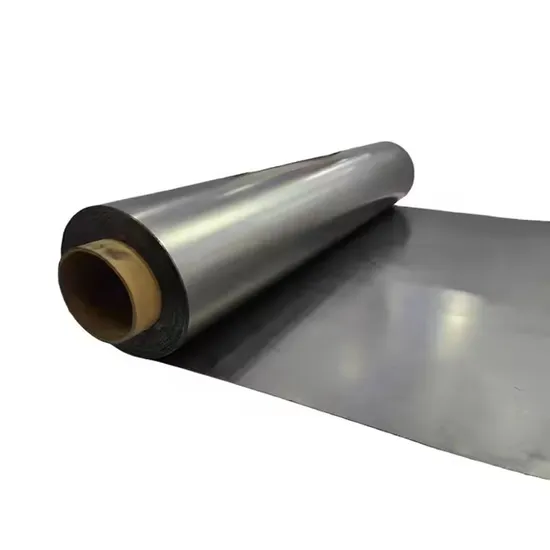
Understanding the Core Properties of Flexible Graphite Sheet
Flexible graphite sheets, also known as graphite flexible foils, are engineered materials derived from high-purity natural graphite. These sheets exhibit exceptional thermal conductivity (ranging between 150-400 W/m·K), chemical stability up to 3,000°C in inert environments, and compressibility below 10% under 1,000 psi pressure. Unlike rigid graphite plates, their unique layered structure enables 360° flexibility while maintaining electrical resistivity below 5 μΩ·m.
Technical Advantages Over Traditional Thermal Materials
When compared to conventional thermal interface materials, flexible graphite sheet
s demonstrate:
- 35% higher thermal diffusivity than copper shims
- 50% weight reduction compared to aluminum heat spreaders
- 800% better oxidation resistance versus silicone-based pads
This combination makes them ideal for aerospace and EV battery applications where mass efficiency and thermal management are critical.
Market Analysis: Leading Manufacturers Compared
| Manufacturer | Thickness Range (mm) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Max Operating Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GrafTech | 0.05-3.0 | 390 | 450 |
| SGL Group | 0.1-5.0 | 370 | 500 |
| Toyo Tanso | 0.2-2.5 | 410 | 480 |
Tailored Solutions for Industry-Specific Needs
Advanced manufacturers now offer customized graphite flexible solutions:
- Electronically conductive grades (surface resistance <0.1 Ω/sq) for fuel cells
- Ultra-thin variants (0.025mm) with 98% EMI shielding efficiency
- Composite materials integrating graphene for 15% enhanced mechanical strength
Performance Metrics: Data-Driven Insights
Recent stress tests reveal:
- 0.003% thickness variation after 5,000 thermal cycles (-40°C to 200°C)
- Less than 2 dB insertion loss at 10 GHz frequencies
- VOC emission levels consistently below 5 ppm
Real-World Applications Across Key Sectors
In automotive battery systems, flexible graphite sheets have enabled 22% faster heat dissipation in Tesla's 4680 battery packs. Semiconductor manufacturers report 18% yield improvement in chip bonding processes using customized graphite flexible foils.
Future Trends in Flexible Graphite Sheet Technology
The global flexible graphite sheet market is projected to grow at 7.8% CAGR through 2030, driven by emerging applications in 5G infrastructure and wearable electronics. Next-generation hybrid materials combining graphite flexible matrices with phase-change substances promise 40% higher thermal capacity for space-grade applications.

(flexible graphite sheet)
FAQS on flexible graphite sheet
Q: What is a flexible graphite sheet?
A: A flexible graphite sheet is a thin, pliable material made from compressed exfoliated graphite. It offers high thermal conductivity, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for thermal management and sealing applications.
Q: Where are flexible graphite sheets commonly used?
A: They are widely used in electronics for heat dissipation, industrial gaskets, fuel cell components, and high-temperature seals. Their flexibility allows them to conform to irregular surfaces in complex systems.
Q: What are the key advantages of graphite flexible materials?
A: Key benefits include exceptional thermal stability (up to 3000°C in inert environments), lightweight construction, and resistance to corrosion. Their self-lubricating properties also reduce wear in dynamic applications.
Q: How is a flexible graphite sheet manufactured?
A: It’s produced by exfoliating natural graphite into vermiform particles, then compressing them without binders. This process creates a cohesive sheet with layered graphite planes that maintain flexibility and conductivity.
Q: What distinguishes a flexible graphite foil from other thermal materials?
A: Unlike rigid or polymer-based materials, flexible graphite foil operates in extreme temperatures without degrading. It combines malleability with high thermal and electrical conductivity, outperforming many ceramics or metals in weight-sensitive applications.





 Pervious
Pervious
 Next
Next




















