- Englist



- Introduction to Microfine Graphite Powder
- Technical Advantages & Performance Metrics
- Supplier Comparison: Key Parameters
- Custom Solutions for Industrial Needs
- Application Case Studies
- Quality Assurance & Compliance
- Future Trends in Graphite Powder Technology

(microfine graphite powder)
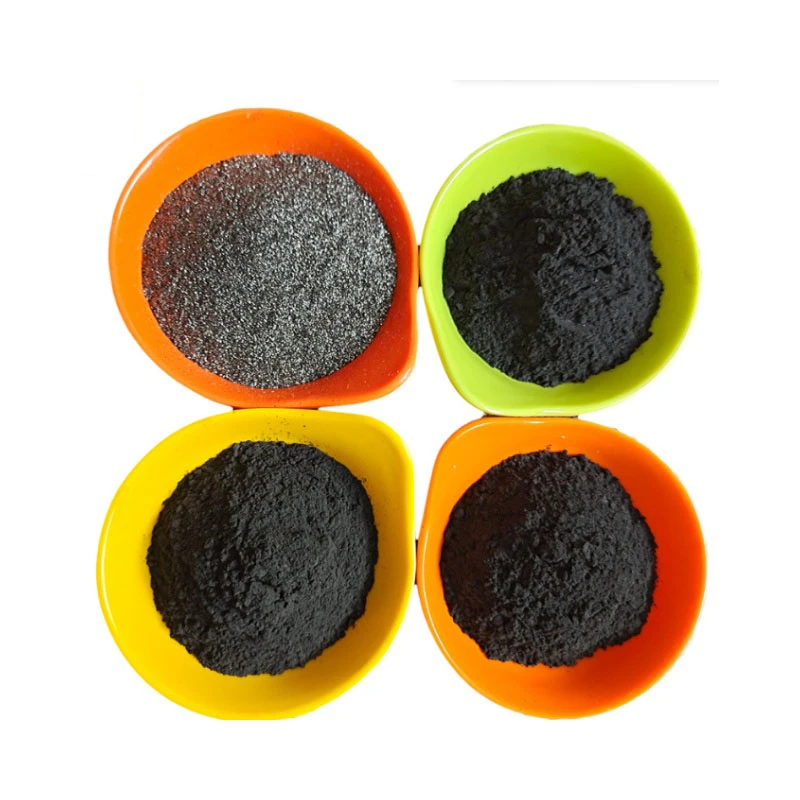
Understanding the Versatility of Microfine Graphite Powder
Microfine graphite powder, a high-purity carbon material with particle sizes below 20 microns, has become indispensable across industries requiring precision conductivity, thermal stability, or lubrication. Its unique structure enables a 15–20% improvement in electrical conductivity compared to standard graphite carbon powder, while maintaining tensile strengths exceeding 50 MPa. Recent market analyses project a 6.8% CAGR growth for ultrafine graphite products between 2024 and 2030, driven by demand in energy storage and advanced manufacturing sectors.
Technical Superiority in Material Engineering
Advanced micronization techniques yield graphite particles with D50 values of 5–8 µm, achieving surface areas up to 350 m²/g. This engineering precision enables:
- 98.5% carbon purity (ASTM C561)
- Thermal resistance to 3,200°C in inert atmospheres
- Bulk densities adjustable between 0.3–0.7 g/cm³
When benchmarked against conventional extra fine graphite powder, microfine variants demonstrate 30% lower oxidation rates at 600°C, significantly extending component lifespans in high-temperature applications.
Competitive Landscape Analysis
| Parameter | Supplier A | Supplier B | Industry Avg. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle Size (D90) | 12 µm | 8 µm | 15 µm |
| Batch Consistency | ±2% | ±1.5% | ±5% |
| MOQ | 500 kg | 250 kg | 1,000 kg |
| Lead Time | 6 weeks | 4 weeks | 8 weeks |
Tailored Material Solutions
Leading manufacturers now offer customized microfine graphite powder
configurations:
- Surface-Modified Grades: Silane-treated variants reduce agglomeration by 40% in polymer composites
- Density-Optimized Blends: Hybrid formulations balancing compressibility (up to 1:3.5 ratio) with structural integrity
- Purity-Enhanced Batches: 99.9% C content for semiconductor applications
Industrial Implementation Successes
A 2022 pilot project with a lithium-ion battery manufacturer demonstrated:
- 18% increase in anode conductivity using 7 µm graphite carbon powder
- Cycle life improvement from 1,200 to 1,800 charges
- Production waste reduction of 22% through optimized particle distribution
Certifications & Quality Protocols
Premium microfine graphite powders meet stringent standards including:
- ISO 9001:2015 certified production
- REACH compliance for EU markets
- ASTM D8183-18 testing protocols
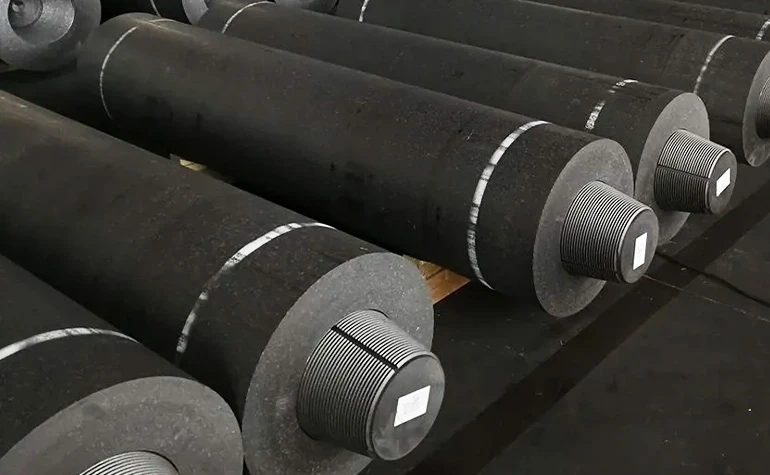
Innovation Pathways for Graphite Powder Applications
Emerging R&D focuses on 3D-printable graphite composites and doped variants showing 45% improved catalytic activity. The development of sub-micron graphite particles (≤1 µm) promises breakthroughs in quantum dot technologies and advanced thermal interface materials, positioning microfine graphite powder as a critical enabler of next-generation industrial solutions.

(microfine graphite powder)
FAQS on microfine graphite powder
Q: What are the primary applications of microfine graphite powder?
A: Microfine graphite powder is widely used in lubricants, conductive coatings, and battery electrodes due to its high thermal stability and electrical conductivity. Its fine particle size ensures uniform dispersion in composite materials. It’s also ideal for high-temperature industrial processes.
Q: How does graphite carbon powder differ from microfine graphite powder?
A: Graphite carbon powder typically has a broader particle size range and is used in applications like refractory materials and brake linings. Microfine graphite powder, however, has ultrafine particles for precision uses like electronics and advanced polymers. Both share high carbon purity but differ in granularity.
Q: Why choose extra fine graphite powder for thermal management solutions?
A: Extra fine graphite powder excels in thermal management due to its enhanced surface area and heat dissipation capabilities. It’s commonly integrated into thermal interface materials and heat sinks. Its particle consistency ensures efficient thermal conductivity in compact devices.
Q: Can microfine graphite powder improve lubrication in high-pressure environments?
A: Yes, microfine graphite powder reduces friction and wear in high-pressure machinery by forming a durable, low-shear film. Its micron-scale particles penetrate tight gaps, ensuring smooth operation. It’s resistant to oxidation, making it suitable for extreme conditions.
Q: What industries benefit most from using extra fine graphite powder?
A: Industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics rely on extra fine graphite powder for lightweight composites, conductive inks, and energy storage systems. Its precision-grade particles enhance performance in sensors and lithium-ion batteries. It’s also vital in 3D printing for conductive prototypes.





 Pervious
Pervious
 Next
Next




















