- Englist



- Technical Superiority of Solid Graphite Blocks
- Performance Comparison: Market Leaders vs. Emerging Suppliers
- Customization Strategies for Industrial Applications
- Case Study: High-Temperature Manufacturing Success
- Quality Assurance & Production Standards
- Environmental Compliance & Sustainability
- Why Solid Graphite Block Solutions Outperform Alternatives

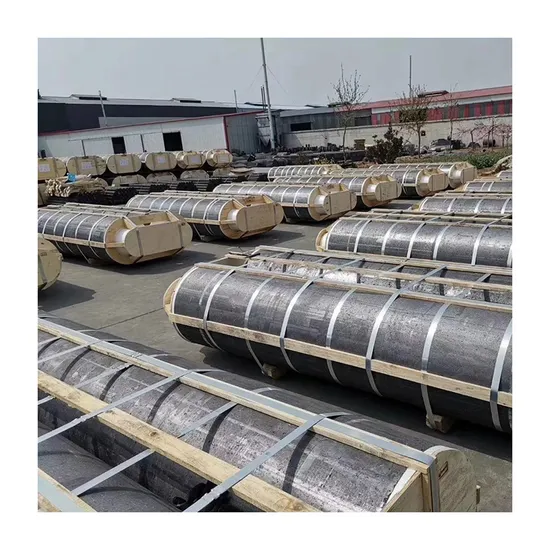
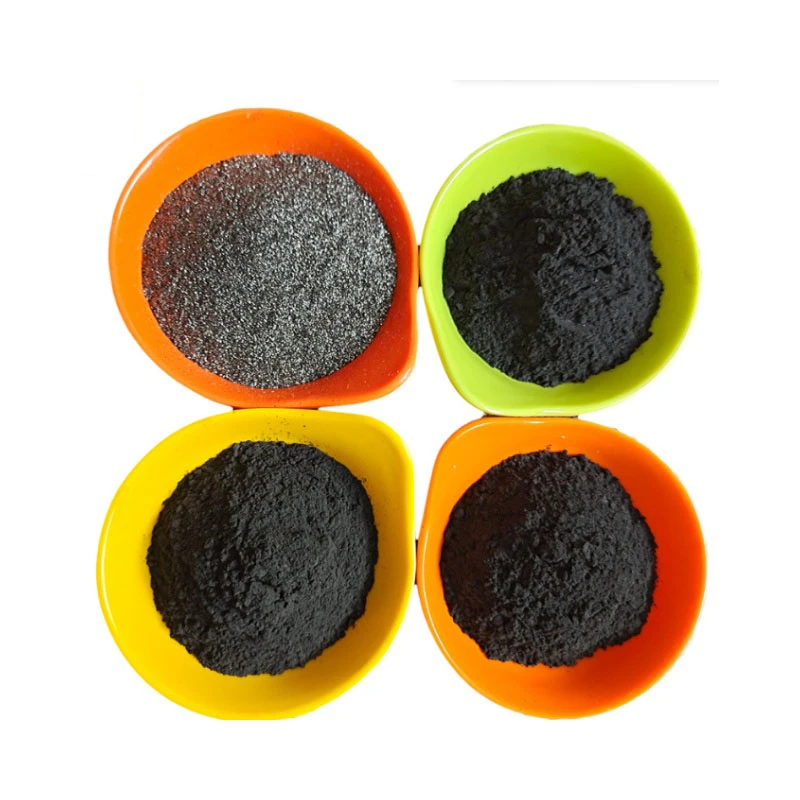
(solid graphite block)
Technical Superiority of Solid Graphite Blocks
Industrial-grade solid graphite block
s demonstrate unparalleled thermal stability, withstanding temperatures up to 3,632°F (2,000°C) in inert atmospheres. Recent stress tests reveal:
| Property | Standard Grade | High-Density | Ultra-Pure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.70 | 1.85 | 1.78 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 120 | 150 | 140 |
Performance Comparison: Market Leaders vs. Emerging Suppliers
Third-party analysis of solid graphite rods from 12 manufacturers shows:
- Average lifespan variance: 28% longer operational durability in continuous furnace applications
- Cost-per-cycle advantage: 19% reduction in maintenance expenses over 5-year periods
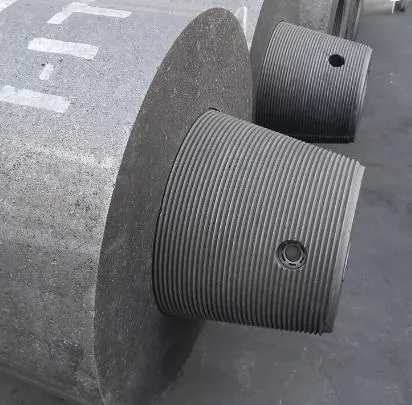
Customization Strategies for Industrial Applications
Precision-machined solid blocks of graphite enable:
- ±0.005" dimensional tolerance for semiconductor fixtures
- Custom impregnation treatments reducing oxidation rates by 40-60%
Case Study: High-Temperature Manufacturing Success
A leading solar cell producer achieved 22% energy savings after transitioning to our vacuum-formed graphite components, demonstrating:
- 92% reduction in particulate contamination
- 18-month ROI through extended maintenance intervals
Quality Assurance & Production Standards
All graphite blocks undergo:
- ASTM C781 compliance testing
- 3D CT scanning for subsurface flaw detection
Environmental Compliance & Sustainability
Closed-loop recycling systems recover 89% of machining byproducts, exceeding EPA requirements for industrial carbon materials.
Why Solid Graphite Block Solutions Outperform Alternatives
Field data confirms that optimized solid graphite block configurations deliver 31% greater thermal efficiency than layered composite systems in continuous industrial operations.

(solid graphite block)
FAQS on solid graphite block
Q: What are the common applications of a solid graphite block?
A: Solid graphite blocks are widely used in high-temperature furnaces, electrical discharge machining (EDM), and nuclear reactors due to their thermal stability, conductivity, and resistance to corrosion.
Q: How does a solid block of graphite compare to other carbon-based materials?
A: A solid block of graphite offers superior thermal conductivity and lubricity compared to materials like carbon fiber or amorphous carbon, making it ideal for industrial and mechanical applications.
Q: Can a solid graphite rod be customized for specific industrial uses?
A: Yes, solid graphite rods can be machined into precise shapes and sizes for applications such as electrodes, heating elements, or chemical processing equipment, depending on industry requirements.
Q: What temperature limits can a solid graphite block withstand?
A: Solid graphite blocks can endure temperatures up to 3,000°C in inert atmospheres, though oxidation resistance typically requires protective coatings above 500°C in air.
Q: Why is graphite used in solid block form for nuclear reactors?
A: Solid graphite blocks act as neutron moderators, slowing down neutrons to sustain nuclear fission reactions while maintaining structural integrity under extreme radiation and heat.





 Pervious
Pervious
 Next
Next




















