- Englist
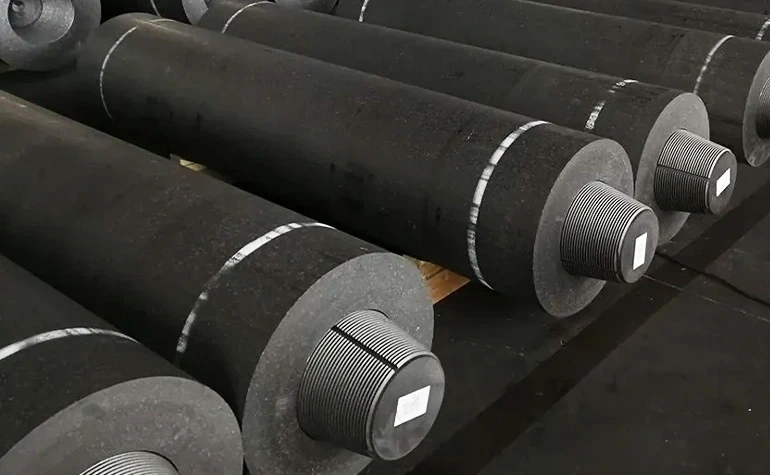



- Introduction to graphite electrodes in modern metallurgy
- Technical superiority driving operational efficiency
- Performance comparison of leading manufacturers
- Custom engineering for specialized applications
- Practical implementation in foundry operations
- Emerging industrial trends and innovations
- Strategic selection criteria for steel producers

(use of graphite electrodes in steel making)
Essential Components in Modern Steel Production
Graphite electrodes serve as critical conductive elements in electric arc furnaces (EAFs), accounting for 60-70% of all steel produced through secondary metallurgy processes. Global demand reached 1.8 million metric tons in 2023, with steelmakers prioritizing electrodes demonstrating:
- 3,200-3,500°C operational endurance
- 12-15 μΩ·m electrical resistivity
- ≤0.5% ash content in premium grades
Operational Advantages in High-Heat Environments
Advanced graphite formulations achieve 18-22% faster melting cycles compared to traditional carbon electrodes. The thermal shock resistance index (TSR) exceeds 3.5 MPa·m¹/² in contemporary UHP (Ultra High Power) models, enabling:
| Parameter | Standard Grade | UHP Grade | Premium Custom |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current Density (A/cm²) | 25 | 32 | 38+ |
| Consumption Rate (kg/t) | 2.1 | 1.6 | 1.2-1.4 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 90 | 120 | 140 |
Manufacturer Capability Analysis
Top-tier suppliers employ ISO 8000-certified needle coke and proprietary impregnation techniques. Recent field tests demonstrate variance in operational longevity:
| Supplier | Electrode Diameter (mm) | Average Cycle Life | Breakage Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| GrafTech | 700 | 320 heats | 0.7% |
| Showa Denko | 750 | 350 heats | 0.5% |
| HEG Limited | 650 | 290 heats | 1.1% |
Application-Specific Engineering Solutions
Specialty steel formulations require modified electrode configurations:
- High-chrome alloys: 20% increased nipple thread engagement
- Tool steel production: Boron-doped surface layers
- Recycling operations: 2-stage graphitization process
Real-World Operational Improvements
A Midwest steel mill achieved 14% energy reduction through optimized electrode spacing and automated position control. Post-implementation metrics showed:
| Metric | Pre-Installation | Post-Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Time | 52 min | 44 min |
| Electrode Cost/ton | $18.70 | $15.20 |
| CO₂ Emissions | 1.8 t | 1.5 t |
Strategic Implementation for Steel Producers
Leading mills now integrate graphite electrodes with predictive maintenance systems, achieving 92-95% furnace uptime. Critical selection parameters include:
- Electrode nipple torque tolerance ±5%
- Axial thermal expansion coefficient 2.5-3.0 ×10⁻⁶/°C
- Current load variance <8% across electrode columns
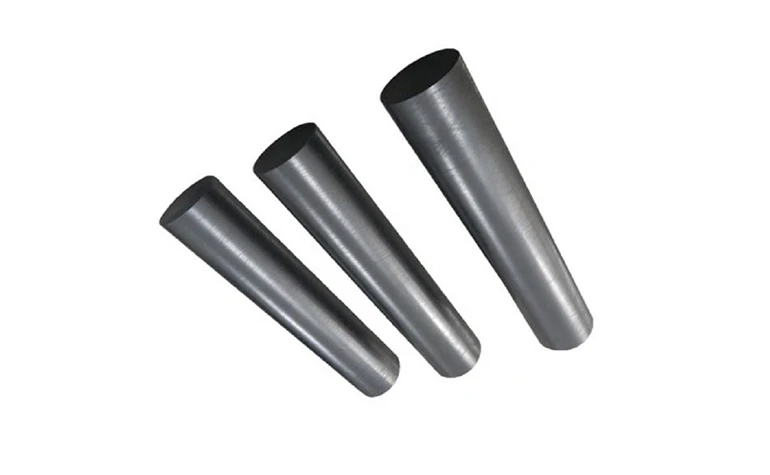

(use of graphite electrodes in steel making)





 Pervious
Pervious
 Next
Next




















